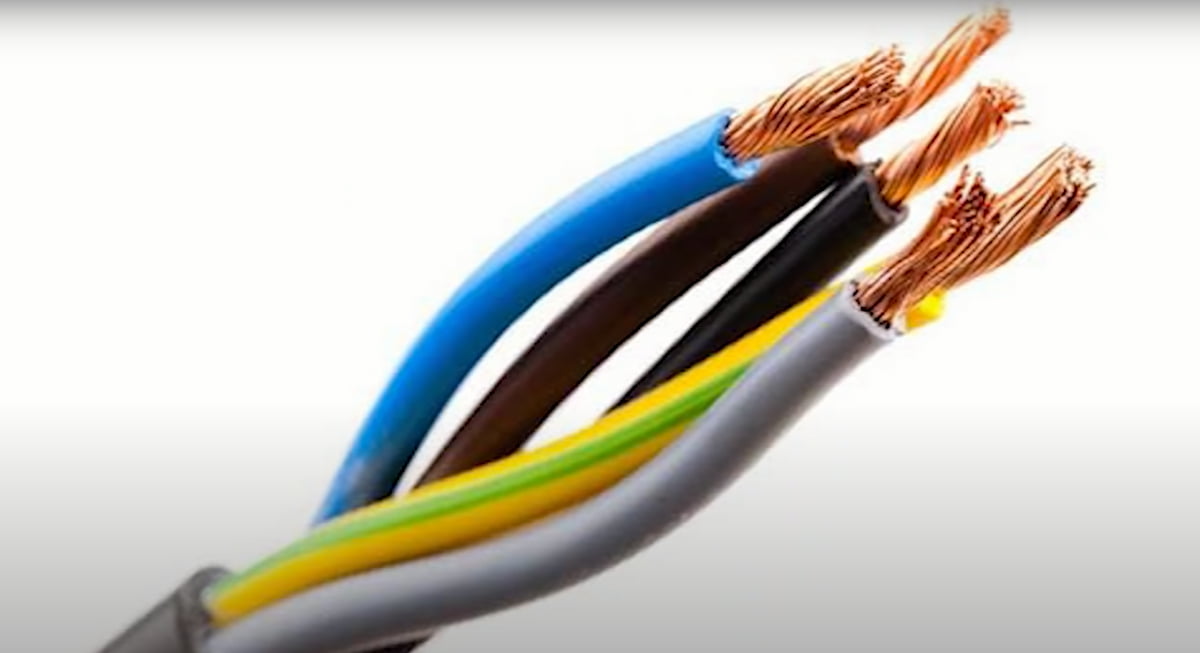
Electrical wire, also known as ‘wire’ or ‘electric cord’, is a flexible electrical conductor with high durability used in electrical wiring. When it is needed, the live wire can provide power to the equipment which supports electrification. With special equipment, the insulated wires can be spliced into other wires to increase the length of the line.
Raw Materials for Electrical Wires
Raw materials for producing wire are mainly iron and copper. The chemical compositions of these two metals are good conductors of electricity because their electrons move easily from atom to atom when exposed to an external electric field. This property makes them superior materials for electromagnetism applications such as appliances, tools, etc.
Moreover, iron has almost ten times higher weight than copper per given volume, this means that more pieces of iron are required to make a given amount of wire compared with copper. As a result, the electric power consumption per unit length is lower for an iron conductor than for a copper one. For electrification purposes, common commercially available wires are made from carbon steel or rubber plastic coatings on copper or aluminium cores.
What is Electrical Cable?
The common electrical cable or electrical wire consists of a number of conductors stranded together with an outer protective layer and its own insulation in between each wire strand. It’s widely used in civil construction areas such as buildings, bridges and so on because it can be easily installed even when being buried underground.
Generally, there is only one electrical cable along the conduit line which collects all its power supplies from different directions through a splitter box at some point. A cable is a multi-core wire that can supply electricity for many devices at home.
Components of an Electrical Wire
An electrical wire has the following components:
- Conductor
- Insulation
- Cable sheathing
The conductor is the electrical wire inside the cable which provides power to the appliances. The insulation layer protects conductors from outside interference and physical damage, reduces leakage of current into surrounding materials and keeps conductor temperatures within safe limits. This layer also adds flexibility as it prevents the wires inside from scratching each other as they move around. It can be made from various products such as rubber plastic coatings on steel, lead sheathings etc.
The shield layer is an outer layer with greater electrical conductivity than those of insulation layers. This shields cables against electromagnetic interference and radio frequency signals. Shield layers often contain braids and metallic meshes that are both electromagnetically conductive and yet flexible. Additional layers of conductive materials may be applied on the outside to protect from abrasion, moisture, sunlight or chemicals.
Electrical Wires in a Civil Area
In the case of electrical cable installation in the civil area, a cable with a watertight sheath is usually needed for better safety. Electrical wires exposed to rain can cause a short-circuit if they’re touching metal objects such as nails or screws used to install the wire into the wall while conducting electricity. In some cases people have been killed by copper exposed live wire that was installed incorrectly by someone else who didn’t know what he/she was doing.
It’s very important not only to choose an appropriate type of wiring but also to hire reliable electricians when installing electrical cables and wires at home. You can hire a professional electrician to do the job for you and avoid problems in the future.
How does Wire Become Live?
When we turn on the power supply switch, electricity flows from batteries or other energy sources through conductors such as copper conductors and steel core into appliances such as radio to generate electromagnetic fields which enables us to hear voices from radio stations through speakers. The reason why those appliances don’t light up when we turn on the switch is that those devices use switches called a relay, capacitor, transformer etc.
They only allow a small amount of current flow from a hot wire for safety reasons since too much current may cause fires. For example, when turning on the power supply switch of your TV, one side press relay may be activated for less than 0.01 seconds and then immediately deactivated after that small amount of current has flowed into CRT TV to turn it on very quickly before shutting off again shortly.
Electrical Wires and Cables Structure
Different types of electrical cable use different types of cores which are made up of metals such as copper or aluminium. The most common wires used in household wiring installations have a solid or strand-like copper core inside an insulation layer that is covered by a metallic cable sheathing known as a “shield” to protect it from outside interference and physical damage while giving it more tensile strength. There are also some electrical cables with a stranded aluminium core that are used for lightweight household appliances.
What is a Ground Wire?
The ground wire is a current-carrying conductor that helps to provide an electrical path to earth or ground through a system of connecting conductors and equipment. It’s also often called Earth (E) or Green/Safety (S). When we turn on power switches, electricity flows from hot wires through the light bulb and back into the circuit box via the metal frame of the ceiling fan or sprinkler etc.
A ground wire (E) is essentially a safety device that allows electrical current to be conducted into the earth or into the ground for the protection of people and property. It can also be used to reduce or prevent voltage drops in wiring systems. A fault induced by say, an earthed metal vehicle on a buried cable would allow current to flow along the surface of the earth rather than through the insulation layer which may cause harm to people who might come in contact with it while repairing or operating any household appliances.

Where does a Bare Ground Wire Connect to?
The electrical wire is always connected to the ground rod firmly using an appropriate grounding clamp before installing any type of metal wires inside walls since they are likely to become live during certain situations such as when touching grounded objects or if hit by lightning etc. It’s advised that cable wire connections be thoroughly done and devices such as circuit breakers and fuses are installed according to local and national electrical codes.
The type of wire that you use may depend on the total amperage of electricity that is required by each appliance. A 40-watt light bulb needs a current below 13 amps but a 1000-watt heater requires a massive current of up to 100 amps, so it’s important to consider this before choosing appropriate wiring for different appliances at home.
What is a Neutral Wire?
The neutral wire is a current-carrying conductor that helps to provide an electrical path to the ground in a system of connecting conductors and equipment. It’s also often called White (W) or Neutral (N)
It’s advised that there is only one hot wire in every electrical circuit, which is responsible for powering all devices connected to it when you turn on switches. The neutral wires help with this process by completing the electrical circuit so electricity can flow throughout your home. If there are more hot wires carrying power into your home, then they would cancel each other out and nothing in your house would work.
A ground and a neutral aren’t always present in small appliances such as lamps and shavers. Small appliances may not require any neutral wire at all since current is usually supplied by the metal casing of the appliance.
Do You Know Why Electricians Use Special Gloves When Working With Live Wires?
Electrical shock occurs when your body comes in contact with any voltage source. An electrician can get injured if he/she touches faulty wiring while inspecting it with bare hands. Therefore, he may wear thick rubber gloves which are connected to a wired safety switch in order to cut off the power supply in case of emergency. Rubber gloves may protect their hands from getting shocked by live wires when they touch them during the installation or inspection process.
What is a ‘Knob and Tube’ Wiring?
The earliest type of electrical wiring used old-fashion way was called knob and tube wiring which was installed in homes at the beginning of the 20th century before an era known as the ‘branch circuit’. It uses a basic system of overhead wires supported on porcelain insulators attached to walls with ceramic knobs, metal tubing or other mechanical protection on cross arms outside on rooftops, insulated joints made with wooden splices embedded in wet plaster inside walls covered with cloth tape.
The reason why electricity can travel quickly through metal tubing is that metal has low resistance values. The advantage of knob and tube wiring is that there’s enough space for air to circulate so it can cool the wires while protecting them from overheating.
What is a Stranded Wire?
Stranded wires are made up of many thin strands of metal with each strand coated in insulation. This design provides greater flexibility for electricians to make the most out of the space inside walls and cabinets compared to the solid wire which can be difficult to bend or twist around corners. However, stranded wires are less effective at transmitting electrical currents due to their steel core, so it’s not used for wiring circuits that require high amperage.
What is a Bare Copper Wire?
Bare copper wires with a thin coat of insulation are called solid wire and it’s the most commonly used in home wiring because it transmits currents easily, is more economical and the bare wire is more flexible than other types of wires. The same applies to the bare ground wire. The electrical wire is also easy to install since one end can be pushed through a small hole in electrical boxes and the other end fastened to the appropriate crew or clip.
What are NM Cables?
Non-metallic (NM) cables are another type of electrical wire that can be installed in your home. They consist of a rubber or plastic sheathing and very thin copper insulated wire inside them and they’re flexible and easy to bend and twist around corners, but the sheathing may melt when exposed to extremely high temperatures. NM cables have been used in place of knob and tube wiring since they’re safer due to being resistant to damage caused by rodents, insects, moisture and sunlight.
What is a Coaxial Cable?
A coaxial cable is an electrical wire that has an inner core conductor made of copper or aluminium surrounded by insulation and a tubular outer metal shield. The advantage of using a coaxial cable is that it can be used to carry higher voltages than single insulated wires since the centre wire protects the other components from any external electrical interference. However, a coaxial cable is not recommended for home use because it doesn’t offer much flexibility compared to non-metallic wiring. A coaxial cable is commonly used in buildings that house satellite dishes or antennas.
Which Electrical Wire is Most Common Today?
A modern family home uses a plastic insulated wire which is a cross between a stranded wire and a solid wire. It’s more economical than solid wires but more flexible than the stranded variety. The insulation protects the wire from extreme temperatures and moisture while the many strands make it easy to bend or twist around corners without causing damage to its internal components.
A Modern Electrical Wiring System
Modern homes use a combination of different types of electrical wiring because it provides the best solution for a home’s location and design. For example, knob and tube wiring can be installed if there’s not enough space for metal conduits or NM cables which are commonly used for outdoor home installation where they’re more resistant to moisture and rodents.
In new homes, a plastic insulated wire is used because it’s modern and most cost-effective. Meanwhile, the most commonly used electrical wire in-home wiring today is a stranded wire with insulation on each strand of metal to protect from overheating. Solid wires are also commonly used but they’re not as flexible or easy to install as their multi-stranded counterparts.